To-do lists are a lifesaver for many of us, whether it’s juggling work tasks, grocery shopping, or planning a weekend getaway. But let’s face it, it’s 2023 and having a paper list stuck to your fridge isn’t cutting it anymore. You need something that syncs across devices, sends you timely reminders, and perhaps even lets you collaborate with others.
That’s where this article comes in. We’ve sifted through an ocean of apps to bring you some of the best ones out there for both your browser and smartphone.
Whether you’re a student keeping track of assignments, a project manager overseeing multiple teams, or just someone trying to keep their life in order, there’s an app here for you.
What makes a great to-do list app?
So, what’s the deal with to-do list apps? I mean, you could scribble tasks down on a post-it note or even use the classic pen and paper method, but come on, we’re in the digital age. An effective to-do list app needs to be a lot more than a digital sticky note. So, before we dive into the list of top contenders, let’s get a grip on what makes a to-do list app genuinely useful.
First off, it needs to be easy to use. No one wants to spend an hour figuring out how to add a simple task. The interface should be intuitive, and getting a new task onto that list should take seconds, not minutes. Heck, you should be able to do it while you’re in line for coffee or waiting for a meeting to start. Many of the apps I’ll mention later have simple, clean interfaces and quick-add features, so you’re not bogged down by unnecessary steps.
Now, let’s talk about the meat and potatoes: features. A good to-do list app isn’t just a checklist. You’ve got to be able to categorize tasks, set deadlines, and prioritize what needs to get done now and what can wait. And yeah, notifications are key. An app that reminds you of what you need to do beats having to manually check it. But it’s not just about nagging you to finish stuff. These apps also help you sync your tasks across different platforms. So, if you add a task on your work computer, you should be able to see it on your phone later, no hiccups.
And last but definitely not least, let’s talk about scalability and integrations. Maybe right now, you’re just organizing grocery lists and workout plans. But what if you’ve got a side hustle or start a small business? The app should grow with you, offering more advanced features like project management or team collaboration. Plus, it should play nice with other apps you’re using. Imagine a to-do list app that syncs with your email, calendar, or even Slack. It’s like having a personal assistant right in your pocket.
Alright, so that’s the rundown on what to look for. Now, let’s get into the specifics and see which apps really knock it out of the park.
Todoist
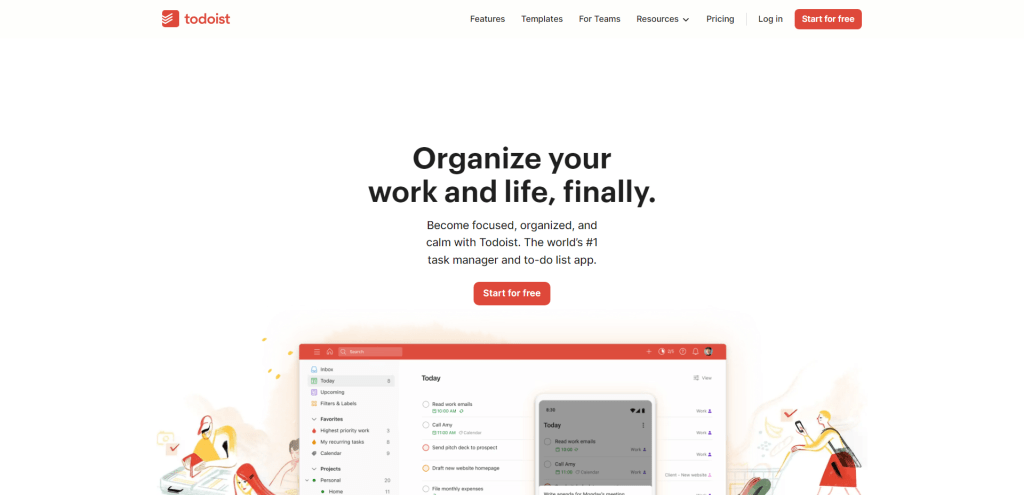
Todoist, a powerful cross-platform task management tool, offers an extensive range of features to help you stay organized and productive. As a browser-based app, Todoist is easily accessible from any device with an internet connection, allowing you to manage your tasks seamlessly across multiple platforms.
One of the key strengths of Todoist lies in its integration capabilities. It connects with popular apps such as Google Calendar, Slack, and Dropbox, enabling you to streamline your workflow and keep all your important information in one place. By integrating with these tools, you can create tasks directly from emails or messages, attach files to tasks, and even sync due dates with your calendar.
Collaboration is another essential aspect of Todoist. You can share projects with colleagues or family members and assign tasks to specific individuals. This feature makes it an ideal choice for teams working together on projects or for managing household chores. Furthermore, Todoist provides real-time updates on tasks’ progress, ensuring everyone stays informed about their responsibilities.
To help you prioritize your tasks efficiently, Todoist offers a flexible labeling system that allows you to categorize tasks based on their importance or context. You can also set deadlines and recurring due dates to ensure nothing slips through the cracks.
In addition to its core features, Todoist boasts a sleek user interface that’s easy to navigate and visually appealing. The app also supports offline access so that you can manage your tasks even without an internet connection.
Trello
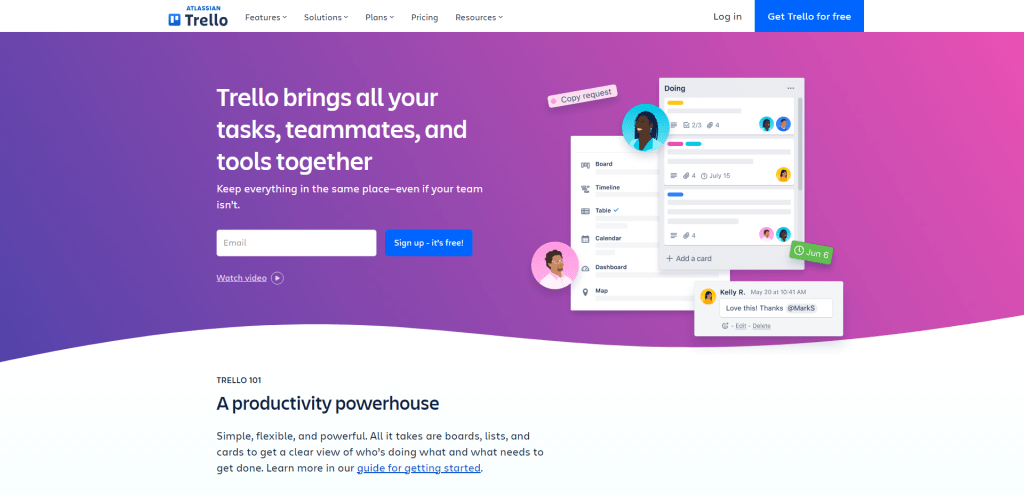
Trello, a popular browser-based to-do list app, stands out for its visual project management approach using boards, lists, and cards. This intuitive system is designed to help you organize tasks, collaborate with team members, and keep track of progress in a visually appealing way.
At the core of Trello’s functionality are boards, which serve as the main workspace for your projects. You can create separate boards for different projects or areas of focus. Each board consists of multiple lists that represent various stages or categories within the project. For example, you might have lists for “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Completed.”
Within each list are individual cards that represent tasks or items to be accomplished. These cards can be easily moved between lists by dragging and dropping them into the desired location. This visual representation allows you to quickly see what tasks are pending, in progress, or completed.
One of Trello’s strengths is its flexibility. You can customize your boards and lists to fit your specific needs and workflow preferences. Additionally, you can add labels, due dates, checklists, attachments, and comments to cards for more detailed task management.
Collaboration is another key feature of Trello. You can invite team members to join your board and assign specific tasks to individuals by adding them as members of a card. Teammates can then update their progress on tasks by moving cards between lists or adding comments directly on the card.
Trello also offers integration with various third-party apps such as Google Drive, Slack, and GitHub through its Power-Ups feature. This allows you to extend Trello’s capabilities even further by connecting it with other tools you already use.
Google Tasks
Google Tasks is a straightforward to-do list app that seamlessly integrates with Gmail and Google Calendar, making it an excellent choice for users who rely on these Google services. With its user-friendly interface, you can easily create, manage, and complete tasks without getting overwhelmed by too many features.
One of the main advantages of Google Tasks is its integration with Gmail. You can create tasks directly from your email inbox by selecting an email and clicking the “Add to Tasks” button. This allows you to keep track of important emails that require action and ensures that you won’t forget about them.
Additionally, Google Tasks syncs with Google Calendar, so you can view your tasks alongside your calendar events. This feature helps you visualize your schedule and due dates more effectively. You can also set reminders for tasks, ensuring that you stay on top of your responsibilities.
The simplicity of Google Tasks means that it’s easy to get started – just sign in with your Google account, and you’re ready to go. You can create multiple task lists for different projects or categories, making it easier to stay organized. Moreover, adding subtasks enables you to break down larger tasks into smaller, manageable steps.
Another useful feature is the drag-and-drop functionality which allows you to reorder tasks based on priority or due date quickly. The mobile app for Android and iOS devices lets you manage your tasks on-the-go so that you can stay productive even when away from your computer.
Microsoft To Do

Microsoft To Do offers a comprehensive task management solution that seamlessly integrates with Outlook. This powerful app is designed to help you efficiently manage your tasks, whether they are personal or work-related.
One of the key features of Microsoft To Do is its smart suggestions. As you use the app, it learns from your habits and preferences, providing tailored recommendations for new tasks and prioritizing your existing ones. This intelligent feature ensures that you can focus on what’s most important without getting overwhelmed by an endless list of tasks.
In addition to smart suggestions, Microsoft To Do boasts a strong integration with Outlook. This means that any tasks created in Outlook will automatically sync with your To Do list, making it easier than ever to stay organized and on top of your responsibilities. Furthermore, this integration allows you to convert emails into tasks directly from your inbox, ensuring that no important action items slip through the cracks.
Another notable aspect of Microsoft To Do is its user-friendly interface. The app allows you to create multiple lists for different purposes (such as work projects or personal errands), making it simple to categorize and manage various tasks. You can also set due dates, reminders, and even add notes or attachments to each task for easy reference.
Moreover, Microsoft To Do supports cross-platform functionality, which means you can access and manage your tasks from any device with an internet connection. Whether you’re using a desktop computer at work or a smartphone on-the-go, this app ensures that your to-do list is always at your fingertips.
Asana
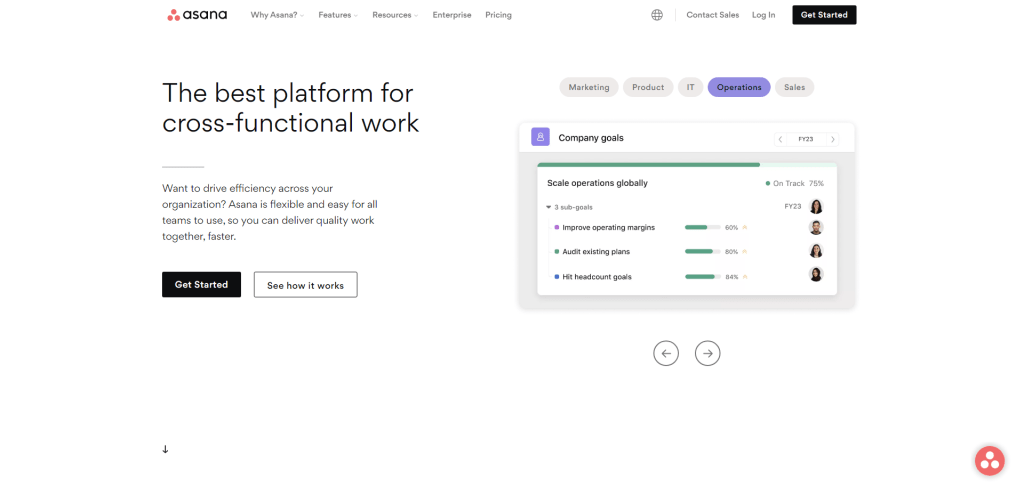
Asana is a versatile project and task management tool designed for teams, offering customizable workflows that help streamline your projects. With its browser-based interface, you can easily access your tasks and collaborate with team members from any device.
One of the key features of Asana is its flexibility in organizing tasks. You can create projects, assign tasks to team members, set due dates, and track progress using various views such as lists, boards, or calendars. This flexibility allows you to customize the workflow according to your team’s preferences and the nature of the project.
Collaboration is another strong suit of Asana. You can add comments to tasks, attach files, and mention team members within the app. This enables seamless communication among team members and ensures that everyone stays on the same page.
Moreover, Asana offers powerful integrations with popular tools like Slack, Google Drive, Dropbox, and more. These integrations allow you to connect your existing tools with Asana for a more efficient workflow.
In addition to its robust task management features, Asana also provides useful reporting and analytics tools. You can generate visual reports on project progress or track individual performance using custom dashboards. This helps you identify bottlenecks in your process and make data-driven decisions for improvement.
Lastly, Asana offers a free plan for small teams with up to 15 members which includes basic features like task assignments and project creation. For more advanced features like custom fields or priority support, you may opt for their paid plans.
ClickUp
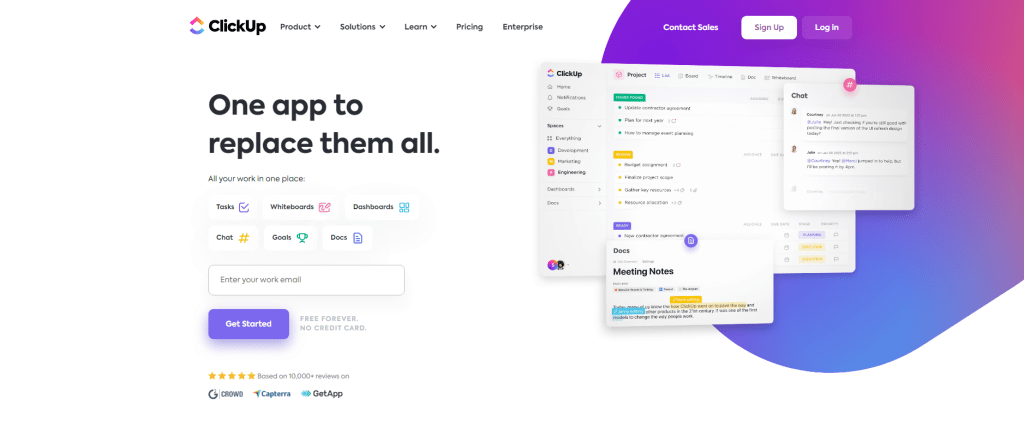
ClickUp is a versatile productivity platform that goes beyond just being a to-do list app. It offers an all-in-one solution for managing tasks, tracking time, and organizing projects. Designed for individuals and teams alike, ClickUp aims to streamline your workflow and improve efficiency.
One of the standout features of ClickUp is its customizable interface. You can tailor the layout to suit your preferences, choosing from various views such as lists, boards, calendars, or Gantt charts. This flexibility allows you to visualize your tasks in a way that works best for you.
In addition to task management, ClickUp offers several built-in tools designed to boost productivity. For instance, it includes a time tracking feature that helps you monitor how much time you spend on specific tasks or projects. This data can be invaluable in identifying areas where you might need to improve efficiency or allocate resources more effectively.
Collaboration is another strong point for ClickUp. The platform supports real-time communication through comments and notifications, making it easy for team members to stay connected and up-to-date on project progress. You can also assign tasks to individuals or groups and set deadlines or priorities for each task.
Integration with popular apps is another advantage of using ClickUp. The platform can connect with tools like Slack, Google Drive, Dropbox, and many others. These integrations help ensure that all your essential information is accessible within one central hub.
Moreover, ClickUp includes automation capabilities that allow you to create custom workflows based on triggers and actions. This feature helps reduce manual work by automating repetitive tasks and streamlining your processes.
Any.do
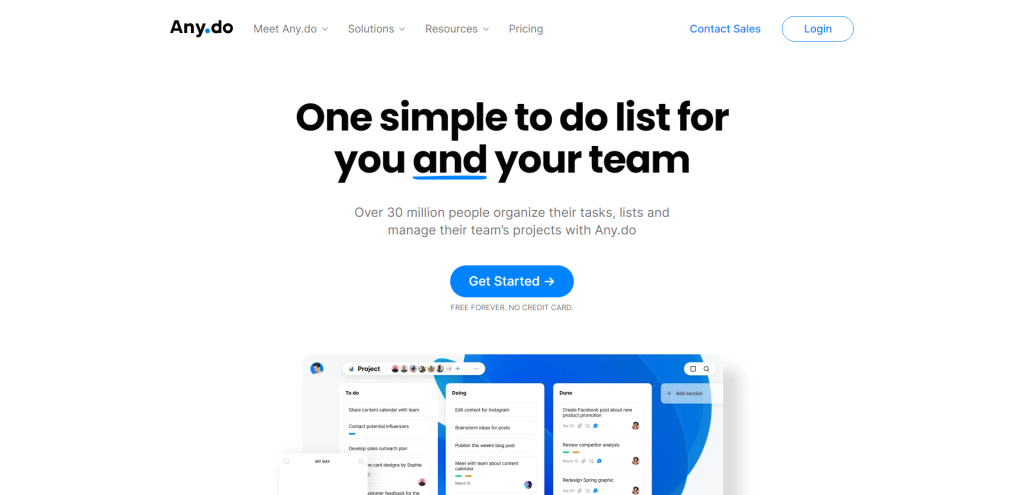
If you’re looking for a to-do list app that not only helps you stay organized but also integrates seamlessly with your calendar, Any.do might be the perfect solution. This task manager is designed to help you manage your tasks efficiently while keeping you on track with reminders and a daily planner.
One of the key features of Any.do is its ability to sync with your calendar. This means that you can view all your tasks and events in one place, making it easier to plan your day and prioritize your workload. Any.do supports integration with popular calendar services like Google Calendar, Apple Calendar, and Outlook.
Reminders
Any.do ensures that you never miss an important deadline or event by sending timely reminders. You can set up one-time or recurring reminders for each task, which can be customized based on time or location. For example, you can receive a reminder when you arrive at a specific location or when it’s time to start working on a particular project.
Daily Planner
The daily planner feature in Any.do helps you make the most of each day by providing an overview of your tasks and events. You can review your schedule for the day and rearrange tasks as needed to ensure that everything gets done efficiently. The planner also allows you to add new tasks quickly so that nothing slips through the cracks.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
Any.do is available on multiple platforms, including web browsers, iOS, Android, and even smartwatches like Apple Watch and Wear OS devices. This means that no matter where you are or what device you’re using, you’ll have access to your tasks and reminders.
Collaboration Features
If you need to collaborate with others on projects or share tasks with family members, Any.do has got you covered. You can easily share lists, assign tasks to others, and even add comments for better communication and collaboration.
Intuitive Interface
Any.do boasts a clean and user-friendly interface that makes it easy to navigate and manage your tasks. The app uses a simple drag-and-drop system for organizing tasks, making it simple to prioritize and rearrange items as needed.
Remember The Milk

Remember The Milk (RTM) is a classic to-do list app that has been helping users stay organized since 2004. With its intuitive interface and powerful features, it’s an excellent choice for managing tasks and staying on top of your daily responsibilities.
Firstly, RTM allows you to categorize your tasks using tags. By assigning tags to your tasks, you can easily filter and sort them based on specific criteria. For example, you might use tags like “work,” “personal,” or “urgent” to quickly identify the tasks that require your immediate attention. This feature enables you to customize your task management approach and ensures that important tasks don’t get lost in the shuffle.
Another standout feature of Remember The Milk is its support for subtasks. Subtasks enable you to break down larger tasks into smaller, more manageable steps. By creating subtasks, you can focus on completing one piece of a project at a time, making it easier to track your progress and stay motivated. Additionally, subtasks help clarify the steps required to complete a task, ensuring that nothing falls through the cracks.
One of the most powerful aspects of RTM is its smart lists functionality. Smart lists are essentially dynamic filters that automatically update based on certain criteria or conditions. For instance, you could create a smart list that displays all tasks due today or another one for tasks tagged as “urgent.” As new tasks are added or existing ones are updated, these smart lists will automatically adjust their contents accordingly. This feature helps keep your task list organized and ensures that relevant information is always at your fingertips.
TickTick
TickTick is a versatile task manager that offers a variety of features to help you stay organized and productive. With its browser-based app, you can easily access your to-do lists and tasks from any device with an internet connection.
One of the standout features of TickTick is its calendar view. This allows you to see your tasks laid out on a monthly, weekly, or daily calendar so that you can visualize your schedule and workload more effectively. You can also sync TickTick with other calendars like Google Calendar or Outlook for seamless integration. This way, you’ll have all your important dates and tasks in one place.
Another useful feature of TickTick is its habit tracker. If you’re looking to develop new habits or break old ones, this tool can help keep you accountable by tracking your progress over time. You can set up specific habits with customized goals and reminders so that you stay on track and motivated.
In addition to task management and habit tracking, TickTick also offers a built-in Pomodoro timer. The Pomodoro technique is a popular time management method that involves working in focused intervals (usually 25 minutes) followed by short breaks. This has been proven to improve productivity by helping users maintain focus while avoiding burnout. With TickTick’s Pomodoro timer, you can easily set up work sessions directly within the app and track your progress throughout the day.
Moreover, TickTick provides other helpful features such as customizable tags for organizing tasks, priority levels for highlighting important items, and collaboration options for working with others on shared projects. These additional tools make it easy for users to tailor the app to their specific needs.
Notion

Notion is an all-in-one workspace designed to cater to various productivity needs. It offers a versatile platform for managing notes, tasks, databases, and collaborative projects. With its user-friendly interface and customizable features, Notion provides an efficient solution for individuals and teams looking to streamline their workflow.
As a powerful note-taking tool, Notion allows you to create rich-text documents with images, videos, and even code snippets. You can easily organize your notes using folders and sub-folders while also taking advantage of the advanced search functionality to find specific content.
For task management, Notion offers a flexible system that supports simple checklists as well as more complex project boards with customizable views like Kanban or calendar layouts. You can create tasks with due dates, assignees, tags, and priority levels. Plus, you can set up reminders so that you never miss a deadline.
One unique feature of Notion is its database functionality. You can create databases in various formats such as tables or galleries to store information like contacts or inventory items. These databases can be linked together using relational properties which enable you to create intricate systems tailored specifically for your needs.
Collaboration is at the core of Notion’s design philosophy. The platform allows multiple users to work on the same document simultaneously with real-time updates. This makes it ideal for teams working on collaborative projects such as brainstorming sessions or planning meetings. Furthermore, you can easily share documents with others by generating public or private links.
In addition to its browser-based version, Notion also offers native apps for Windows, macOS, iOS and Android devices. This ensures seamless synchronization across devices so that you can access your workspace anytime and anywhere.
Summary
Alright, you’ve made it through the maze of to-do list apps, features, and what you should really be looking for. At the end of the day, a solid app can be a game-changer for productivity, but only if it fits your lifestyle and needs. It’s like finding the perfect pair of sneakers; it has to fit right, feel comfortable, and let you move how you want. So, don’t just jump on the first app you come across. Take a minute to think about what you actually need from it, then go ahead and give a couple of them a spin.
So what’s the next step? Dive in. Most of these apps have free versions or trials, so the only thing you’ve got to lose is, well, disorganization. Test a few out, mess around with the features, and see which one makes your life easier.
And hey, if the first one doesn’t hit the mark, don’t sweat it. Just move on to the next until you find your perfect match. After all, the aim here is to make your life simpler, not complicated. Happy tasking!
