The ubiquity of Microsoft Excel in the world of data management is hard to ignore. Yet, the cost of an Office 365 subscription is not something everyone can justify, especially when all you need is a reliable spreadsheet program. So, what if you could get your hands on a free software that stands up well against the Excel juggernaut?
In comes a roster of impressive free alternatives, designed to meet your data-crunching needs without gouging your wallet. These platforms offer a range of features, from basic data entry and calculations to advanced analytics and visualizations. Whether you’re a small business owner, student, or an aspiring data analyst, there’s a suitable alternative waiting for you.
Why be tethered to a costly subscription when there are potent and free options available? In this article, we’ll dig into the top free Excel alternatives, dissect their strengths and weaknesses, and help you identify the one that’s the perfect fit for your unique requirements. The aim? To offer you the freedom to manage and analyze data, all without spending a dime.
Google Sheets
Google Sheets stands as a powerful tool in the realm of spreadsheet software. This web-based application, developed by Google, is designed to allow users to create, edit, and share spreadsheets online. It’s a part of Google’s productivity suite, Google Workspace, and integrates seamlessly with other tools in the suite. With its user-friendly interface and robust features, Google Sheets has become a popular choice among individuals and businesses seeking an efficient way to handle data.
The strength of Google Sheets lies in its ability to facilitate real-time collaboration. Multiple users can work on the same spreadsheet simultaneously, making it an ideal tool for team projects and group tasks. Changes are saved automatically and can be tracked easily, ensuring smooth workflow and accountability.
Key Features
- Real-Time Collaboration: This feature allows multiple users to access and edit the same spreadsheet simultaneously. Users can see who else is viewing or editing the document at any given time.
- Integration with Google Workspace: Being part of Google Workspace means that Sheets integrates seamlessly with other tools in the suite like Docs, Slides, Drive etc., providing a unified productivity platform.
- Powerful Data Analysis Tools: Google Sheets comes equipped with various data analysis tools such as pivot tables, conditional formatting and charting options that allow users to manipulate data effectively.
Pricing: Google Sheets is available for free for personal use with a basic Google account. For businesses or professional use that needs more advanced features like custom email domain or more storage space on Drive, there are paid plans available under Google Workspace subscriptions starting from $6 per user per month.
LibreOffice Calc

LibreOffice Calc is an open-source spreadsheet software that forms part of the LibreOffice suite, a powerful and free office suite used by millions of people around the world. As an open-source software, it is developed and maintained by a community of developers who work to continually improve its features and capabilities. LibreOffice Calc offers a wide array of mathematical functions, making it an excellent tool for anyone needing to perform complex calculations or data analysis.
The software is designed with versatility in mind; it’s suitable for everything from simple tasks like keeping track of household expenses to more complex uses such as organizing data for business reports or scientific research. It’s fully compatible with other spreadsheet programs, including Microsoft Excel, allowing users to easily transfer data between different platforms.
Key Features
- Wide Range of Mathematical Functions: LibreOffice Calc supports a vast array of mathematical functions, allowing users to perform complex calculations with ease.
- Data Analysis Tools: The software includes tools for statistical and scientific data analysis, making it suitable for use in various fields such as business, finance, and research.
- Compatibility: LibreOffice Calc is compatible with other spreadsheet programs like Microsoft Excel. This feature allows users to import and export files in different formats without losing any data or formatting.
Pricing
As an open-source tool, LibreOffice Calc is completely free to download and use. There are no subscription fees or hidden charges associated with its use. Users can freely download the software from the official LibreOffice website and start using it immediately without any restrictions.
Zoho Sheet
Zoho Sheet is a cloud-based spreadsheet application that offers a robust alternative to traditional spreadsheet software. It is part of the Zoho Office Suite, a comprehensive collection of productivity tools developed by Zoho Corporation. This tool has been designed to facilitate seamless collaboration and data analysis, with an array of features that make it easy to manage and interpret data. Its AI-powered data cleaning features set it apart from many other spreadsheet applications, offering users the ability to efficiently streamline and clean their data.
The primary appeal of Zoho Sheet lies in its cloud-based nature. This allows for real-time collaboration between team members, regardless of their location. Changes made by one user are instantly visible to others, eliminating the need for constant back-and-forth communication and version control issues. Furthermore, being a web-based application means that users can access their spreadsheets from any device with an internet connection.
Key features
- AI-Powered Data Cleaning: One of the standout features of Zoho Sheet is its AI-powered data cleaning capabilities. This feature allows users to automatically detect and rectify inconsistencies in their data, saving valuable time and effort.
- Real-Time Collaboration: As a cloud-based application, Zoho Sheet enables real-time collaboration between users. Multiple people can work on the same spreadsheet simultaneously, making it ideal for team projects.
- Integration with Other Zoho Apps: Zoho Sheet integrates seamlessly with other apps in the Zoho suite, such as Zoho CRM and Zoho Projects. This allows for streamlined workflow across multiple platforms.
For pricing, there are several options available based on your needs:
- Free: Provides basic spreadsheet functionalities along with 5GB storage
- Standard: Priced at $3/user/month (billed annually), it offers additional integrations, automation capabilities, and 100GB storage per user
- Professional: Priced at $6/user/month (billed annually), it provides advanced analytics tools along with 1TB storage per user
Whether you’re looking for an alternative to Excel or just want to try something new, give Zoho Sheet a shot – you might just find what you’ve been looking for.
Apache OpenOffice Calc
Apache OpenOffice Calc is a robust, open-source spreadsheet software that serves as an excellent alternative to Microsoft Excel. Developed by the Apache Software Foundation, it’s part of the Apache OpenOffice suite, which includes several other productivity tools. The software offers a comprehensive range of features that cater to both basic and advanced spreadsheet users. It’s designed to be compatible with Microsoft Excel, which means you can easily import and export Excel files without worrying about formatting issues or data loss.
The strength of Apache OpenOffice Calc lies in its powerful computation capabilities and flexibility. It’s equipped to handle complex mathematical functions and large datasets, making it an ideal tool for data analysis and financial modeling. Moreover, being an open-source software, it invites a community of developers to continually improve and update its features, ensuring that it stays relevant in the ever-evolving tech landscape.
Key features
- DataPilot: This feature allows users to pull in raw data from external databases and cross-tabulate, summarize, and convert it into meaningful information.
- Scenario Manager: With this feature, you can create “what if” scenarios for performing complex forecasts and analyses.
- Natural Language Formulas: This user-friendly feature lets you use standard English rather than cryptic codes for creating formulas.
When it comes to pricing, one of the most attractive aspects of Apache OpenOffice Calc is that it’s completely free. Being an open-source tool means there are no licensing fees or subscription costs involved. All you need is a device with an operating system like Linux, Windows, or Mac OS X to download and install the software. The freedom from cost makes Apache OpenOffice Calc an appealing choice for individuals as well as small businesses operating on a tight budget.
EtherCalc

EtherCalc is a powerful online spreadsheet tool that has been crafted with collaboration at its core. This web-based application allows multiple users to simultaneously edit and interact with spreadsheets in real-time, providing an effective platform for team-based tasks and projects. EtherCalc is designed to provide a seamless blend of individual productivity tools with advanced features that facilitate cooperative work.
This software brings the power of desktop spreadsheet programs to the web, allowing you to access and modify your data from any device with an internet connection. It’s not just about convenience though, EtherCalc’s collaborative features make it a fantastic tool for teams who need to work together on complex data sets or calculations. The ability for multiple users to edit the same spreadsheet in real-time can greatly speed up project completion times and improve overall efficiency.
Key Features
- Real-Time Collaboration: EtherCalc allows multiple users to simultaneously edit the same spreadsheet. Changes are instantly visible to all users, making it ideal for team-based tasks and projects.
- Web-Based: As a web-based tool, EtherCalc can be accessed from any device with an internet connection. There’s no need for any software installation which makes it highly convenient.
- Open-Source: EtherCalc is open-source software, meaning its code is freely available for anyone to use or modify. This encourages community-driven development and improvement of the platform.
Pricing
EtherCalc is completely free to use! As an open-source project, it relies on community support rather than commercial sales or subscriptions. All you need is an internet-connected device and you’re good to go!
WPS Office Spreadsheets
WPS Office Spreadsheets is a robust and user-friendly alternative to Microsoft Excel. Developed by Kingsoft, it is part of the WPS Office suite that also includes tools for word processing and creating presentations. This spreadsheet tool stands out for its comprehensive range of features that are not only easy to use but also fully compatible with Microsoft Excel. Whether you are an individual seeking to organize personal data or a business aiming for efficient data management, WPS Office Spreadsheets can cater to your needs.
The software’s compatibility with Excel extends beyond just being able to open and edit Excel files. It also emulates Excel’s user interface, making it easy for those accustomed to Excel to transition smoothly. But it doesn’t stop at mimicking its more famous counterpart; WPS Office Spreadsheets brings its own unique strengths into play, offering a compelling package that can hold its own in the crowded field of spreadsheet software.
Key Features
- Full Compatibility with Microsoft Excel: WPS Office Spreadsheets supports all file formats used by Microsoft Excel (from 97/2000/2003/2007/2010). This means you can open, edit, and save files in these formats seamlessly.
- Abundant Templates: The software comes with numerous free templates to help you create various types of spreadsheets quickly and easily. These templates cover multiple scenarios including budget planning, project management, invoice creation and more.
- Data Analysis Tools: WPS Office Spreadsheets offers a suite of powerful data analysis tools including pivot tables and data visualization features that allow users to analyze complex data sets effectively.
Pricing
WPS Office Spreadsheets offers both free and premium versions. The free version provides basic functionality which is sufficient for most personal users. For more advanced features such as VBA support, extensive file format support, and absence of ads, you can upgrade to the Premium version which costs $29.99/year or $79.99 for a lifetime license.
Gnumeric

Gnumeric is a robust, free spreadsheet program developed by the GNOME project. As part of the GNU Project, it was designed with the goal of being the best possible spreadsheet tool. Gnumeric’s strength lies in its powerful computation abilities and high-degree of accuracy. It’s a great option for users who require advanced data analysis features without needing to invest in premium spreadsheet software.
The software is open-source, meaning that its source code is freely available for modification and distribution. This results in a software that continues to improve and adapt over time, thanks to the contributions from developers all around the world. Gnumeric aims to be more than just an Excel alternative; it strives to provide superior computational precision and innovative features that set it apart from other spreadsheet tools.
Key Features
- High Precision Calculation: Gnumeric is noted for its high-level accuracy in complex numerical operations, making it an excellent choice for scientific or financial computations.
- Broad File Compatibility: The software supports a wide range of file formats including Microsoft Excel, OpenDocument, Lotus 1-2-3, and more.
- Extensive Function Library: Gnumeric comes equipped with over 150 functions covering a wide range of mathematical operations.
As for pricing, Gnumeric stands out as an entirely free tool. As part of the GNU Project’s commitment to free software, there are no hidden costs or premium versions – every feature and function is available at no charge to the user.
OnlyOffice Spreadsheet Editor
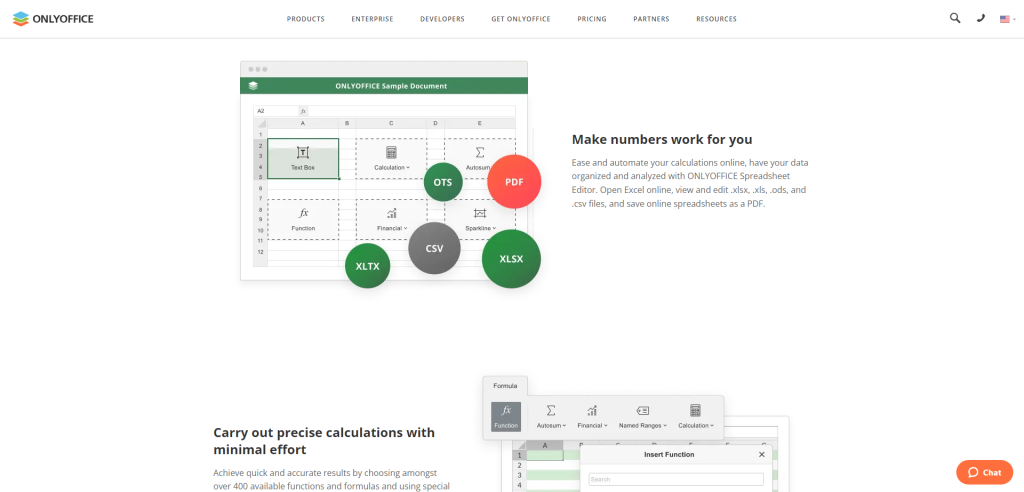
OnlyOffice Spreadsheet Editor is a highly versatile, open-source spreadsheet tool that has been designed to meet the needs of businesses and individuals alike. It is part of the OnlyOffice suite, which is a comprehensive package of office productivity tools. The software provides robust functionality and compatibility with all key formats, including Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets.
The Spreadsheet Editor is designed for ease-of-use and powerful functionality. It leverages advanced technology to deliver a user-friendly interface, while still offering a depth of features that can handle complex spreadsheet tasks. Whether you’re dealing with large datasets or simple tables, OnlyOffice Spreadsheet Editor can cater to your needs.
Key Features
- Broad Compatibility: OnlyOffice Spreadsheet Editor supports all major spreadsheet formats including XLSX, ODS, and CSV. This ensures seamless integration with other tools and easy data migration.
- Powerful Calculation Engine: The software comes equipped with an extensive range of mathematical functions, making it easy to perform complex calculations.
- Collaborative Capabilities: With real-time co-editing features, multiple users can work on the same document simultaneously. This makes it an excellent tool for collaborative projects.
Pricing
While the basic version of OnlyOffice Spreadsheet Editor is free to use, there are also premium versions available for more advanced needs. The Home Server version costs $99/year for unlimited users while the cloud-based version starts at $5/user/month for the Start plan and goes up to $8/user/month for the Business plan.
Quip Spreadsheets
Quip Spreadsheets is a powerful tool that has been designed to bring a new level of efficiency and collaboration to your spreadsheet tasks. It is a part of the Quip productivity suite, which is developed by Salesforce. This software offers an innovative approach to spreadsheet management by integrating real-time collaboration and chat functionalities within the document itself.
Quip Spreadsheets stands out due to its unique blend of traditional spreadsheet functionality with modern communication tools. This integration enables users to discuss data, share insights, and make decisions right within the spreadsheet environment, fostering seamless communication and collaboration amongst team members.
Key Features
- Real-Time Collaboration: Quip Spreadsheets allows multiple users to work on the same sheet simultaneously. Changes made by any user are instantly visible to all collaborators, ensuring everyone stays on the same page.
- Integrated Chat Functionality: With this feature, users can discuss data points directly within the document. This eliminates the need for switching between different applications for discussions and decision making.
- Seamless Integration with Other Quip Tools: Quip Spreadsheets can be effortlessly integrated with other tools in the Quip productivity suite such as Quip Docs and Slides.
Pricing
Quip operates on a subscription-based pricing model. The Starter plan costs $10 per user per month while the Enterprise plan costs $25 per user per month. For larger organizations requiring advanced features and support, custom pricing options are also available upon request.
Smartsheet
Smartsheet is a robust web-based platform designed to enhance project management, reporting, and work management tasks. This powerful tool is engineered to streamline your business operations by providing a single collaborative workspace that can be accessed from any device. Smartsheet’s intuitive interface, coupled with its extensive range of features, makes it an excellent alternative to traditional spreadsheet applications like Microsoft Excel.
The software’s core function revolves around its spreadsheet-like interface that enables users to plan, track, automate, and report on work. It offers the familiarity of a spreadsheet but with the added benefits of a database-driven application. Smartsheet has been adopted by numerous organizations across various industries due to its ability to facilitate collaboration and improve efficiency.
Key Features
- Collaborative Work Management: Smartsheet provides comprehensive work management capabilities that encourage team collaboration. Users can share sheets for simultaneous editing, attach files from Google Drive or Dropbox, set up automated alerts and reminders, and even assign tasks within the sheet itself.
- Dynamic Reporting: The software offers robust reporting tools that allow users to create summary reports across multiple sheets. Users can visualize their data using charts and graphs or export reports in various formats including PDF and Excel for further analysis.
- Automation & Integration: Smartsheet supports automation of repetitive tasks such as sending reminders or moving rows between sheets based on specific triggers. Furthermore, it integrates with popular apps like Slack, Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, Salesforce among others which helps in streamlining workflows.
Pricing
Smartsheet operates on a subscription-based pricing model with plans starting at $14 per user per month when billed annually. They also offer Business ($25/user/month) and Enterprise plans whose pricing is available upon request. A free trial is available for those who wish to explore the software before committing to a subscription.
Summary
In the end, the notion that Microsoft Excel is the irreplaceable king of spreadsheets could use some reconsideration. As we’ve seen, there’s a diverse landscape of free alternatives that offer a compelling array of features, covering everything from basic data manipulation to complex analytics. While each has its own set of pros and cons, what they all share is the ability to handle your data management tasks without the financial burden of a subscription.
So, what’s the takeaway here? Don’t feel obliged to stick with Excel out of habit or the mistaken belief that it’s your only viable option. Whether you’re managing a budget, plotting a research project, or conducting a deep dive into big data, there’s likely a free tool out there tailored to your needs. It’s high time we embrace these cost-effective alternatives and the new opportunities they bring.
