Oracle has issued a stern warning about critical vulnerabilities across many of its products, emphasizing the urgency for organizations to install the latest security patches immediately. In its July patch round, Oracle released 386 new security updates, several of which addressed vulnerabilities with an impact score of 9.8 out of 10.
“Several of these vulnerabilities are remotely exploitable without requiring authentication, which means attackers can exploit them over a network without needing user credentials,” Oracle stated in their advisory. The affected products span a wide range, from Oracle’s Communications suite—including Billing and Revenue Management and Cloud Native Core Automated Test Suite—to other critical systems like WebLogic Server, MySQL Cluster, and Siebel CRM Deployment.
Historically, WebLogic Server has been a prime target for cyber attackers, with vulnerabilities being exploited shortly after updates are released. Oracle has confirmed ongoing reports of attacks leveraging vulnerabilities that have already been patched, highlighting an issue where customers fail to apply these critical updates promptly.
Unlike companies such as Adobe and Microsoft, which release security updates monthly, Oracle follows a quarterly patch cycle. The next round of updates is scheduled for October 15. This quarterly cadence can leave systems exposed for longer periods, making it even more crucial for organizations to apply patches as soon as they are available.
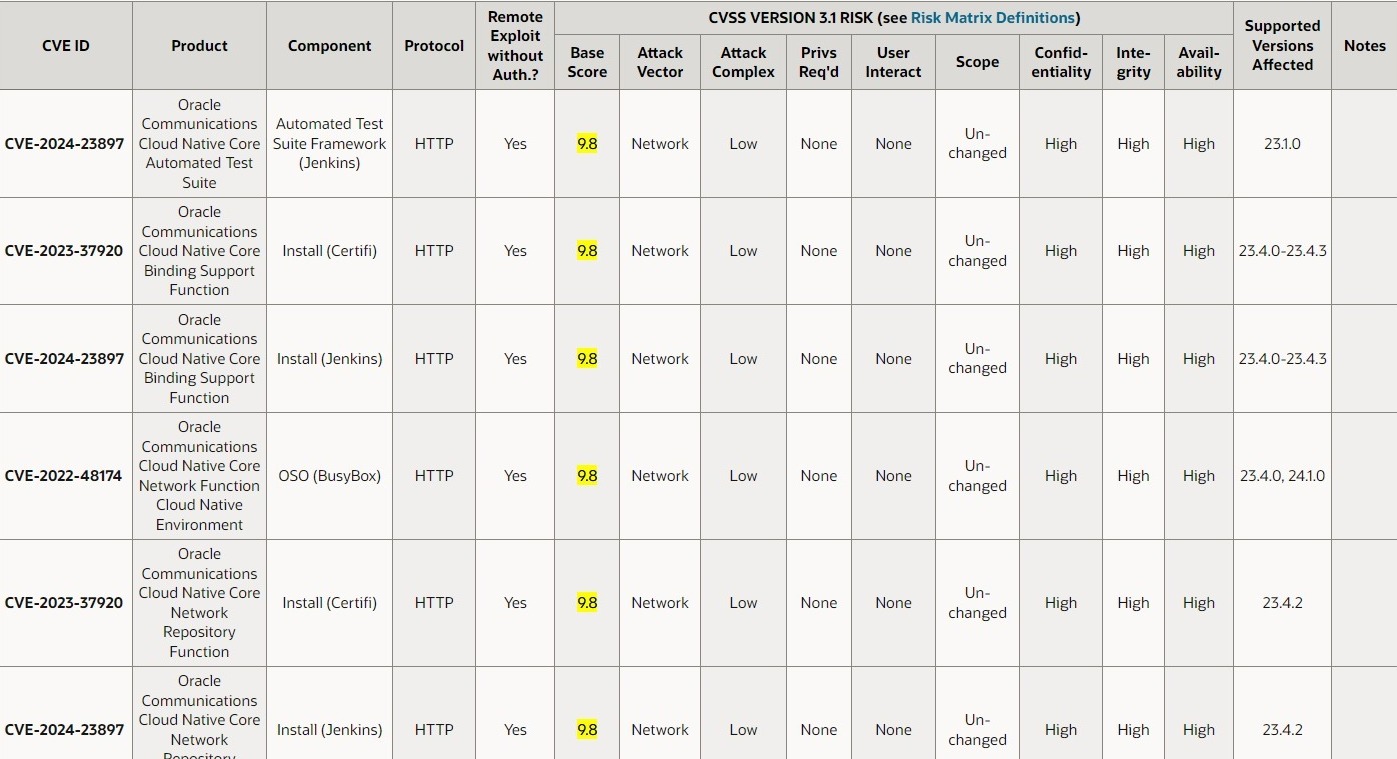
The July 2024 patch round is particularly comprehensive for Oracle Communications, with 95 new security patches. Out of these, 84 vulnerabilities are remotely exploitable without authentication. For instance, vulnerabilities in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core Automated Test Suite and Cloud Native Core Binding Support Function have been assigned the highest severity score, reflecting their critical nature.
Oracle’s detailed Risk Matrix provides insight into the specific vulnerabilities and their potential impacts. Each vulnerability is identified by a CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) ID, which helps organizations understand each issue’s exact nature and risk. For example, CVE-2024-23897 in the Automated Test Suite Framework (Jenkins) and CVE-2023-37920 in the Binding Support Function both present high risks with the potential for remote exploitation.
Oracle’s advisory is clear: “Customers should apply Critical Patch Update security patches without delay.” The company also advises that until patches can be applied, organizations should consider blocking network protocols required by an attack or removing privileges from users who do not need them. However, these are not long-term solutions and could disrupt application functionality.
The consequences of neglecting these updates can be severe. Oracle has documented instances where successful attacks have occurred due to unpatched systems. “Attackers have been successful because targeted customers had failed to apply available Oracle patches,” the advisory notes, underscoring the critical need for timely updates.
Oracle also recommends that organizations stay on supported product versions to ensure they receive necessary patches. Products no longer under Premier or Extended Support are not tested for vulnerabilities, leaving older versions potentially exposed. Upgrading to supported versions is essential for maintaining security.
