In my review of the most popular front-end frameworks – I’ve covered JAMstack as the most popular trend for two years in a row now. Looking at the data on GitHub, there are roughly 20ish SSG projects right now that have more than 1,000 stars. So, the goal of this review is to look at the most popular options, understand what makes them unique, and also learn why they’re so popular.
What are static site generators?
A static site generator (SSG) is a framework that takes content from various sources (such as markdown files or a database) and generates a set of static HTML files. Unlike traditional dynamic websites, which generate HTML on the fly for each request, static sites are pre-generated, allowing them to be served quickly and efficiently.
This makes static site generators well-suited for blogs, documentation sites, and other types of content-focused websites.
Let’s look at the overall rankings.
| SSG | Description | Created | Stars |
|---|---|---|---|
| Next.js | The React Framework | 2016 | 102k |
| Gatsby | The fastest frontend for the headless web, with React. | 2015 | 54k |
| Nuxt | Create type-safe, production-grade apps and websites with Vue 3. | 2016 | 44k |
| Docusaurus | Easy to maintain open source documentation websites. | 2017 | 43k |
| Hexo | A fast, simple & powerful blog framework, powered by Node.js. | 2012 | 36k |
| Astro | Astro is the all-in-one web framework designed for speed 🏝️✨ | 2021 | 28k |
| Eleventy | Transforms a directory of templates (of varying types) into HTML. | 2017 | 14k |
| VitePress | Vite & Vue powered static site generator. | 2020 | 6.9k |
| Nextra | Simple and flexible site generation framework with everything you love from Next.js. | 2020 | 5.5k |
| Outstatic | Static site CMS that lives inside your Next.js install. | 2022 | 1.5k |
Are you surprised to see Next.js in this list? At this rate, not only will Next be the top choice for Node.js frameworks, but also general front-end stuff. The other notable generators in this list are Astro, VitePress (which is the new VuePress), but also Nextra (which is based on Next.js).
Actually, all the listed options are great in their own way, and we’ll do a deep dive into that in this article. But when it comes down to it, the actual thing that SSGs are competing for is performance.
I’ll share the average npm install times for each SSG mentioned in this article. I’m also going to add each project’s node_modules size after the initial installation. Each installation was performed 5 times, including using npm cache clean --force every time. And where possible, I’m going to highlight custom benchmarks.
Let’s start with the most interesting project that’s getting a lot of attention right now.
Astro
npm install: 15.63s v2.1.0 | node_modules: 174 (MB)

Astro is a modern front-end framework designed for building fast, content-focused websites with a new pattern of web architecture called Astro Islands. Unlike other modern frameworks, Astro is 100% HTML with zero JavaScript by default, meaning it removes all unnecessary JavaScript from static HTML pages, leading to exceptional website performance.

Astro Islands supports multiple UI frameworks, which means you can create interactive components using any supported framework.
Astro benchmarks
Over the last couple of days (at the time of writing this), Astro has made a few significant announcements. First, they did a complete overhaul of their design system (spoiler: it’s awesome!), they published a performance report for popular web frameworks, and they shipped Astro 2.1.
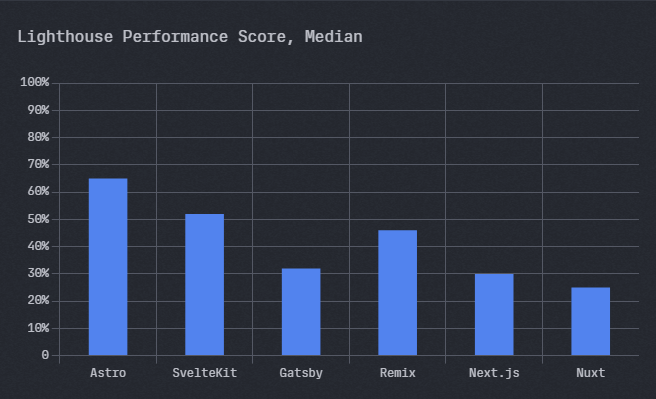
The Astro team has also done independent benchmarks based on the specification that is set by the HTTP Archive’s Web Almanac standards (Lighthouse, P90).
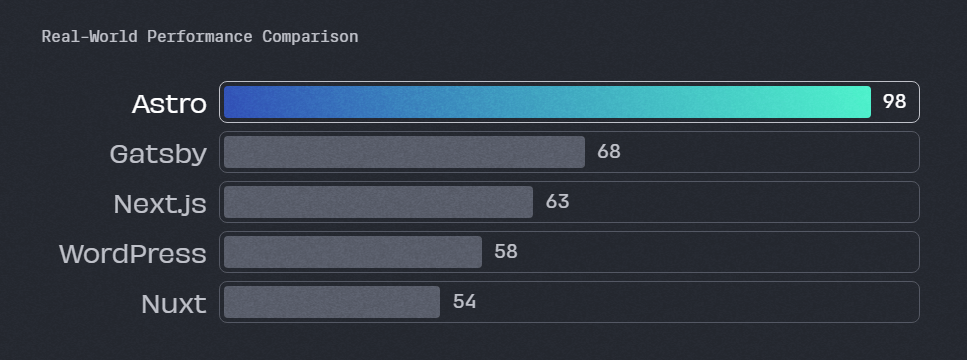
But it’s not just performance and islands; Astro packs a punch in the features department, too.
Building content-first websites
Astro is designed to solve the problems associated with building content-rich websites. This includes most marketing sites, publishing sites, documentation sites, blogs, portfolios, and some e-commerce sites. Astro’s unique focus on content allows it to make tradeoffs and deliver unmatched performance features that wouldn’t make sense for more application-focused web frameworks to implement.
Astro leverages server-side rendering over client-side rendering as much as possible. This approach stands in contrast to other modern JavaScript web frameworks that require client-side rendering of your entire website and include server-side rendering mainly to address performance concerns.
This approach has been dubbed the Single Page App (SPA), in contrast with Astro’s Multi Page App (MPA) approach. The result is amazing web performance for every website, out of the box.
In conclusion, Astro is an all-in-one web framework that comes with everything you need to build a website, but it’s also flexible enough to allow you to extend it with over 100+ integrations like React, Svelte, Vue, Tailwind CSS, MDX, image optimizations, and more. It’s UI-agnostic, which means you can Bring Your Own UI Framework (BYOF), and you can even mix and match different frameworks on the same page.
Eleventy (11ty)
npm install: 8.21s v2.0.0 | node_modules: 36 (MB)

Eleventy has been gaining a lot of popularity, especially among people who are tired of using JavaScript-heavy static site generators. Out of the box, Eleventy is zero-config by default and works with any project structure. It does not require a client-side JavaScript framework, although you can use one if you prefer.
Eleventy encourages progressive enhancement, which means you can focus on providing essential content first and add dynamic functionality step by step. This can help reduce the long time to interactive (TTI) issue that occurs in JavaScript-based static site generators.
Eleventy supports 11 template languages, generates pages quickly, and is pre-rendered by default, which can improve performance. Eleventy is suitable for marketing websites, blogs, documentation, and eCommerce websites with mostly static content. In fact, brands like Google, Red Hat, and many notable tech startups use Eleventy in production!
It’s not a framework.
Instead of being a framework, Eleventy is a tool that generates static pages from templates. It is not tied to any specific front-end or back-end technology, and it does not have any particular way of structuring your web application.
Eleventy is designed to be flexible and to work with the existing structure of your project.
One advantage of Eleventy not being a framework is that it does not require you to learn a particular way of doing things. You can use the tools and libraries that you are familiar with, and you can structure your application in the way that makes the most sense for your project.
This can be particularly useful if you are already using a set of tools and want to add static site generation to your workflow without having to learn a new framework.
Another advantage of Eleventy not being a framework is that it allows for more incremental adoption. You can start using Eleventy on a few templates and gradually add more as you become more comfortable with the tool. This means that you can adopt Eleventy at your own pace, without having to make a complete shift in the way you develop web applications.
Next.js
npm install: 7.31s v13.2.3 | node_modules: 263 (MB)

Next.js is everywhere! Not only is it the fastest-growing JavaScript framework ever, but it’s also packed to the brim with features and persistent releases that quite literally introduce cutting-edge features. Next started as a zero-configuration framework for server-rendered universal JavaScript web apps and over time has evolved to support various features like static site generation, TypeScript, dynamic pages, serverless functions, and more.
The framework is particularly useful for projects that require flexibility in how specific parts of the website are built, and it can be used in a hybrid mode, combining static site generation with dynamic enhancement.
Next.js also includes built-in features like an image component with optimization, support for exporting applications to static HTML, and Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR), which allows you to create or update static pages after building the site.
Data Fetching in Next
The Next 13 version introduced a new app directory, which for the time being, is still in beta and not recommended to use in production. With this new version, Next’s pre-existing Data Fetching (getStaticProps and others) methods are being deprecated and replaced with the new App Router. For now, however, you can still use the legacy data fetching methods.
In Next, getStaticProps is a function that allows you to pre-render pages at build time using data that’s available ahead of a user’s request. This means that the page can be fully rendered with all its content before the user even requests it, resulting in faster load times and better performance.
To illustrate, an example of where getStaticProps might be used is with a headless CMS. A headless CMS separates the content management from the presentation layer, which allows you to work with the content data without worrying about how it’s going to be presented to the user.
With getStaticProps, you can fetch data from the headless CMS at build time and pre-render the page with that data.
When getStaticProps is used, Next.js generates both HTML and JSON files that can be cached by a CDN for performance. The JSON file is used in client-side routing through next/link or next/router, which means that client-side page transitions won’t call getStaticProps again.
This also makes the application faster, as it doesn’t have to re-fetch data that has already been fetched and rendered.
Gatsby
npm install: 47.23s v5.7.0 | node_modules: 585 (MB)

Gatsby is a React-based framework for building websites and apps.
One of the main benefits of Gatsby is its data layer, which allows you to easily pull in data from various sources, such as headless CMSs (Content Management Systems), APIs, and databases.
This data can be combined and queried using GraphQL.
This means that you can use Gatsby to build websites that can pull in data from multiple sources and display it in a unified and consistent manner. Gatsby also provides a large ecosystem of plugins, themes, and starters that can be used to add functionality and customize your project.
As far as performance goes, Gatsby uses static-site generation, deferred static generation, and a custom-built page rendering engine to preload the content that matters, resulting in a snappy website that feels incredibly fast and performant.
Gatsby was acquired by Netlify.
Over the last couple of years, Gatsby has been pushing its cloud services quite hard. So it doesn’t come as a surprise that Netlify took an interest and finally acquired the platform. Kyle Mathews confirmed the news in a blog post last February.
In fact, you now get to deploy your personal Gatsby projects on Netlify for free. You can even use a custom domain name!
Nuxt
npm install: 23.51s v3.2.3 | node_modules: 218 (MB)

Nuxt is a web framework built on top of the popular JavaScript framework, Vue. Nuxt provides developers with a set of powerful features that make web development fast, intuitive, and optimized for user experience. It allows you to build websites and web applications with different rendering strategies, including server-side rendering (SSR), static site generation (SSG), client-side rendering (CSR), and incremental static regeneration (ISR).
Moreover, Nuxt is optimized for performance, with features such as code-splitting, tree-shaking, optimized cold-start, link prefetching, and payload extraction. These features enable fast load times and an overall smoother user experience.
Last but not least, Nuxt has a wide range of modules and plugins available to developers, including those for data fetching, state management, meta tags helpers, route guards, cookies, error handling, and more. You can also integrate Nuxt with popular content management systems (CMS) and user interface (UI) libraries with just one line of code.
Rendering modes
Nuxt supports two rendering modes: client-side only rendering and universal rendering.
In client-side only rendering, the Vue.js application is rendered entirely in the browser after the JavaScript code is downloaded and parsed. This mode is useful for applications that require high interactivity and don’t need indexing. However, it may have performance issues and slower search engine optimization.
Universal rendering, on the other hand, returns a fully rendered HTML page from the server to the browser. This mode provides faster page load times and better SEO, but can be more challenging to develop for and requires a running server. Nuxt uses the concept of “hydration” to add interactivity to the static HTML page returned from the server, enabling a seamless transition to client-side rendering.
In summary, Nuxt provides developers with the flexibility to choose between client-side only rendering and universal rendering modes based on the specific requirements of the application.
Docusaurus
npm install: 27.42s v2.3.1 | node_modules: 136 (MB)
Docusaurus is a static site generator that helps users create documentation sites quickly and easily. It uses MDX, which allows you to write documents and blog posts in Markdown and embed React components within them. It also has built-in localization with support for translations, and you can extend and customize your site’s layout by writing React components.
Docusaurus 2.0 is built with attention to the developer and contributor experience, providing a modern Jamstack documentation site with a single-page application (SPA) and client-side routing. It offers full control over site browsing experience by providing your own React components and can be easily extended with advanced features and plugins.
Design principles & comparisons
Docusaurus has clear design principles, aiming to be easy to learn and use with a small API surface area and intuitive project directory structure. It follows a layered architecture with sensible defaults and no vendor lock-in, allowing users to choose their own Markdown engines, CSS frameworks, and methodologies.
Compared to other static site generators, Docusaurus is unique in its focus on documentation sites and provides many out-of-the-box features, including document versioning, internationalization, and search.
- While Next.js and Gatsby can also help build documentation websites, they require more effort to implement features than Docusaurus.
- MkDocs is a good option for those who do not need a single-page application and do not plan to use React.
- Docsify and GitBook are not static-site generators and are not SEO-friendly.
- Jekyll is a mature tool, but Docusaurus aims to provide a similar developer experience while using modern JavaScript ecosystem tooling to set new standards for doc sites’ performance and ease of setup.
Overall, Docusaurus is a powerful and user-friendly tool for creating documentation sites, with many useful features and a growing community of users. Its support for MDX, React components, localization, document versioning, and Algolia documentation search makes it a valuable tool for developers and engineers looking to build efficient and effective documentation sites.
Hexo
npm install: 6.24s v6.30 | node_modules: 32 (MB)

One of the main advantages of Hexo is its easy setup, requiring only one command to install and create your first project. It also has built-in Markdown support, which is the default choice for Hexo, making it easy to write content without worrying about complex syntax. Hexo has a vast ecosystem and a rich directory full of themes and plugins that extend its functionalities.
Hexo’s plugins feature powerful APIs for limitless extensibility and various plugins are available to support most template engines, such as EJS, Pug, Nunjucks, and many others. Hexo’s rich command-line tool set enables users to create, customize, create a new layout or pages with ease, and also allows users to build and deploy their Hexo site with one command.
Hexo is also SEO-ready, with many amazing SEO features included in its barebone setup. You can extend your options by using SEO plugins to optimize your website for search engines. Hexo has a comprehensive documentation that details everything, starting from how to install its command-line tools, how to set up your website, generate, and publish it, as well as add new pages and layouts with detailed customization options.
VitePress
npm install: 7.43s v1.0.0-alpha.50 | node_modules: 52 (MB)

VitePress is the spiritual successor of VuePress, providing significantly better developer experience, better production performance, a more polished default theme, and a more flexible customization API. While the API difference between VitePress and VuePress mostly lies in theming and customization, the Vue team has decided to focus on VitePress as the main recommended SSG in the long run.
One of the primary use cases of VitePress is for technical documentation, where it ships with a default theme designed specifically for this purpose. It also supports fully customized themes and flexible APIs to load data and dynamically generate routes, making it ideal for building blogs, portfolios, and marketing sites.
VitePress offers a great developer experience when working with Markdown content, powered by Vite. It offers built-in Markdown extensions such as Front-matter, tables, and syntax highlighting, making it an excellent choice for highly technical documentation. Additionally, each Markdown page is also a Vue Single-File Component, enabling interactivity in static content using Vue templating features or imported Vue components.
Generated as a SPA
Unlike many traditional SSGs, a website generated by VitePress is a Single Page Application (SPA), resulting in faster initial load times and better user experience after the initial load. VitePress automatically pre-fetches page chunks for links that are within the viewport, resulting in near-instant post-load navigation.
Moreover, VitePress provides interactivity without penalty. Each Markdown page is processed as a Vue component and compiled into JavaScript, and the Vue compiler separates the static and dynamic parts, minimizing the hydration cost and payload size.
Overall, VitePress is a powerful and flexible SSG that enables developers to build fast, content-centric websites, making it an ideal choice for documentation and other content-driven use cases.
Nextra
npm install: 16.28s v2.2.18 | node_modules: 309 (MB)

Nextra is a simple, powerful, and flexible site generation framework that enables developers to create beautiful websites with Next.js and MDX. It was initially created by Shu Ding and Paco Coursey in 2020, with Yixuan Xu contributing significantly to the project since 2021. In 2022, Dimitri Postolov from The Guild joined the core team to help with the development of version 2.0.
One of the standout features of Nextra is its full-power documentation in minutes. The framework automatically converts Markdown links and images with Next.js Link and Next.js Image, resulting in no slow navigation or layout shift. Additionally, Nextra offers an advanced syntax highlighting solution powered by Shiki, making build-time syntax highlighting performant and reliable.
With Nextra, you can easily create multi-language websites using file-based routing with locales suffixed, as Nextra and Next.js will do the rest. The framework also supports MDX 2, which allows you to use components inside markdown with a huge performance boost since version 1.
Hybrid rendering
In addition, Nextra offers hybrid rendering, allowing you to leverage the hybrid rendering power of Next.js with their markdown content, including SSG, SSR, and ISR.
Nextra first collects all Markdown files and configurations from the pages directory and then generates the “page map information” of the entire site, rendering things such as the navigation bar and sidebar. With Nextra, all .mdx files under the pages directory are rendered with MDX, an advanced Markdown format with React component support.
Overall, Nextra is a powerful and flexible framework that streamlines website development with Next.js and MDX. Its advanced features, such as full-text search and hybrid rendering, make it an ideal choice for developers seeking to create high-performing and accessible websites.
Outstatic
npm install: 14.52s v0.0.36-canary.1 | node_modules: 412 (MB)

Outstatic is a content management system that simplifies website development by providing a user interface for content creation and editing. Unlike traditional systems, Outstatic doesn’t require the setup of a database or server; instead, all data is saved in a GitHub repository.
Outstatic organizes website content into two main parts: Collections and Documents.
Collections are used to categorize and define different types of content, acting as categories. For instance, a blog site would have a “Posts” collection to hold blog posts. Each blog post in the collection would be a document.
Documents are the individual pieces of content that comprise the website. They contain various types of data, such as the title, content, date, status, author, URL slug, description, and cover image. The title is the name of the document, while the content is the main text and images.
The date indicates when the document was published, while the status determines whether it’s visible on the website or not. The author field shows the name and avatar of the document creator, and the URL slug is the address of the document on the website.
Additionally, the description provides a brief summary of the document, and the cover image is an optional image used as a cover or Open Graph image.
Summary
From a static site generator perspective, I believe that the JavaScript community is moving in the right direction by developing more comprehensive solutions that can build full applications without compromising page speed.
While JavaScript frameworks have traditionally been associated with dynamic websites, there’s a fundamental shift happening in the usage of SSGs. However, unnecessary JavaScript code can still be sent to the client, leading to page bloat and slower loading times. The solution to this issue is partial hydration, which allows developers to selectively hydrate only the parts of the web page that require interactivity, rather than sending unnecessary JavaScript to the client.
As static site generators continue to evolve, I’m excited about the potential of bringing these patterns further up into the web platform itself. For example, WebAssembly could allow developers to write a full-stack framework in any language, reducing the gap between frontends and backends and enabling static site generators to use more lightweight, efficient code.
In summary, I think we are moving towards more mature solutions that offer a full toolkit for building full applications, including static site generators. By addressing issues such as page bloat and slow loading times through partial hydration and other techniques, we can improve the performance and user experience of static sites.
